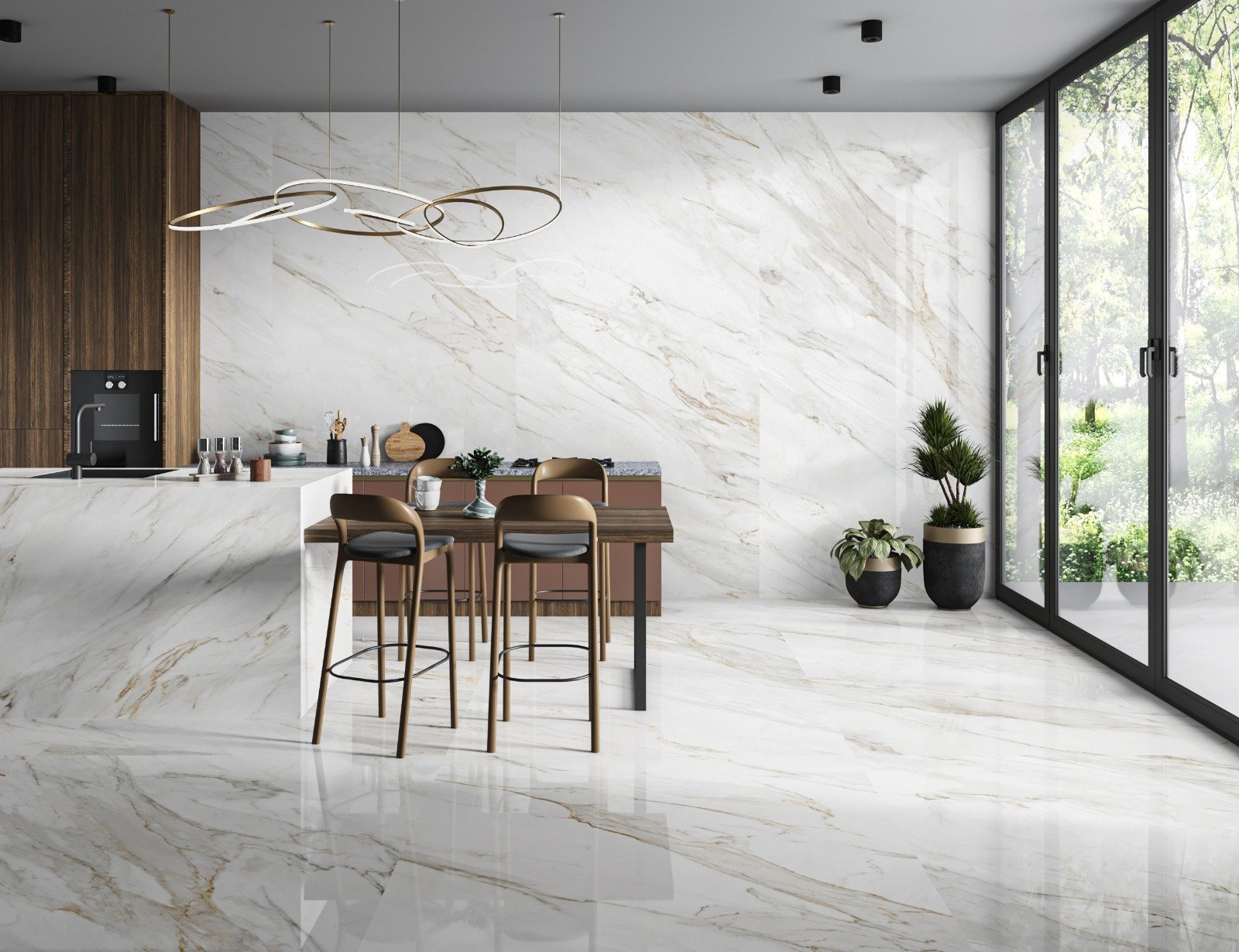
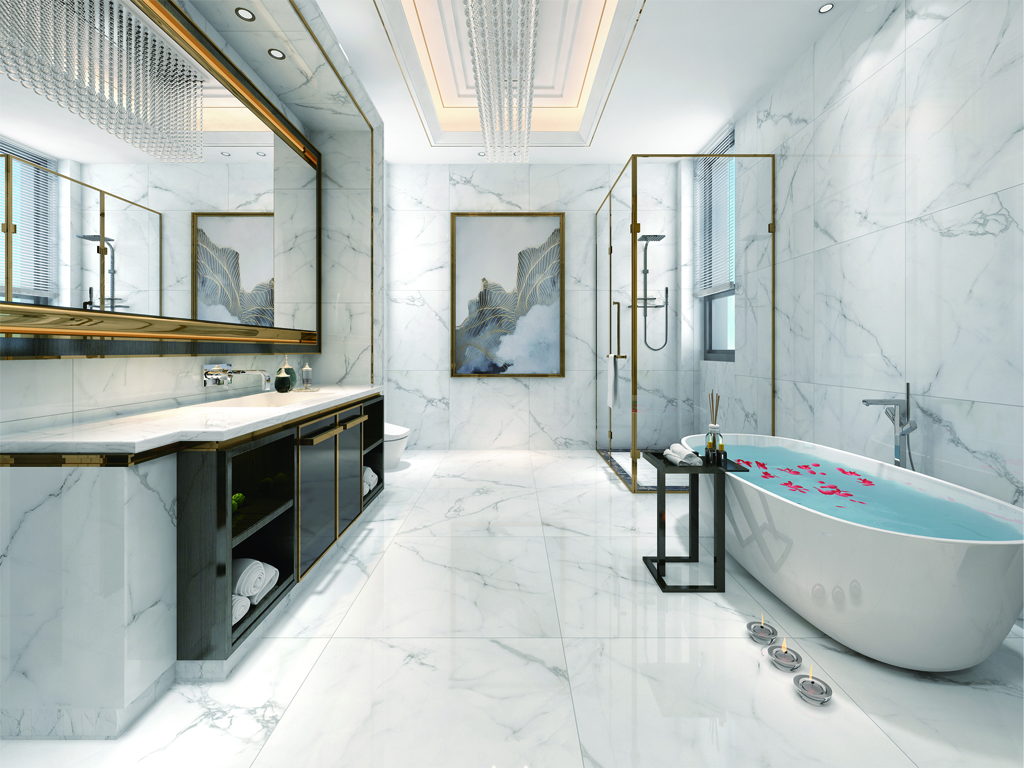
Slab tiles—large-format ceramic or porcelain tiles (typically 600×1200 mm or larger)—are pivotal in modern architecture and design, prized for their durability, aesthetic versatility, and ability to create expansive, cohesive spaces. As demand for high-quality, innovative tiles grows, manufacturers are adopting advanced technologies to enhance production efficiency, material performance, and design precision. This article explores the latest technological advancements in slab tile manufacturing and their impact on improving quality, sustainability, and functionality.
Key Advanced Technologies in Slab Tile Production
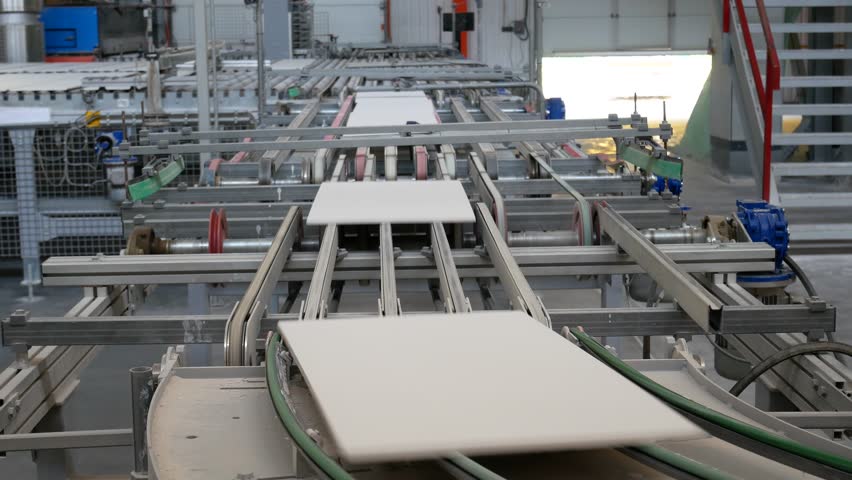

- Digital Printing and Decoration
– High-Resolution Digital Printing:
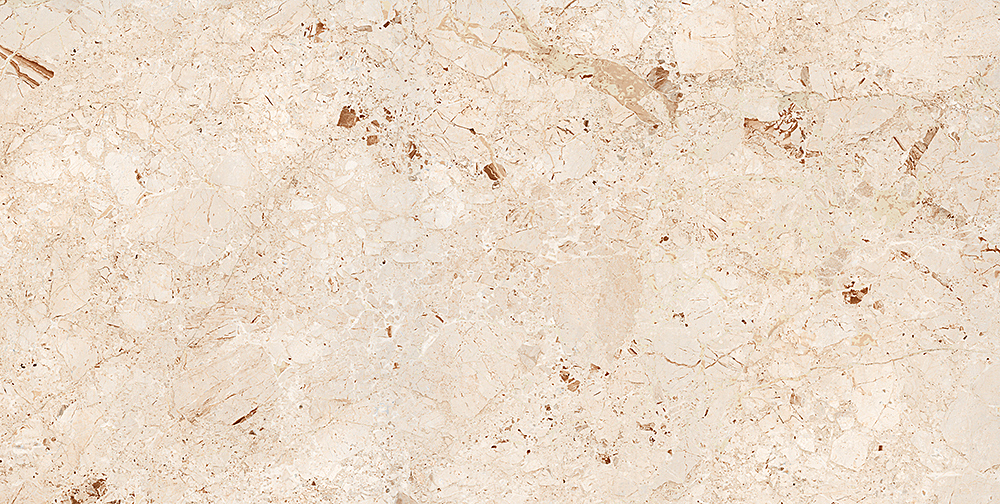
Modern printers with 360° inkjet technology enable hyper-realistic patterns, gradients, and textures (e.g., wood, stone, or abstract art) on large tiles. This technology allows for intricate customization, reducing reliance on natural materials.
– Quality Impact: Precise replication of natural textures enhances visual appeal and reduces defects caused by manual decoration.
– ۳D Printing:
۳D printers create textured surfaces (e.g., stone-like roughness or geometric patterns) directly on tiles, adding depth and tactile interest.
– Quality Impact: Enhances realism and durability compared to traditional glazing.
- Advanced Material Science
– Nano-Coatings and Surface Treatments:
Nanotechnology is used to develop scratch-resistant, stain-proof, and self-cleaning coatings. For example, hydrophobic coatings repel water and dirt, while anti-microbial layers inhibit bacterial growth.
– Quality Impact: Improves longevity and maintenance-free performance in high-traffic areas.
– Porcelain and Composite Materials:
High-density porcelain formulations ensure resistance to thermal shock, chemical exposure, and physical wear. Some tiles incorporate recycled materials (e.g., glass, industrial waste) without compromising strength.
– Quality Impact: Enhances durability and sustainability.
- Automation and Robotics
– Robotic Cutting and Polishing:
Automated systems with laser-guided cutting tools ensure precise, consistent tile dimensions, minimizing waste. Robotic arms handle heavy slabs, reducing human error.
– Quality Impact: Reduces defects and improves edge quality.
– AI-Driven Quality Control:
Machine learning algorithms analyze images of tiles in real-time to detect imperfections (e.g., cracks, color inconsistencies). Defective tiles are automatically rejected.
– Quality Impact: Enhances uniformity and reliability.
- Energy-Efficient Manufacturing
– Low-Emission Kilns:
Advanced kilns with infrared or microwave technology reduce firing times and energy consumption by up to 30%.
– Quality Impact: Faster production cycles without compromising material integrity.
– Solar-Powered Production Lines:
Some manufacturers integrate solar energy to power facilities, lowering carbon footprints.
– Quality Impact: Aligns with eco-conscious consumer demands.
- Smart Tiles and IoT Integration
– Sensor-Embedded Tiles:
Tiles with embedded sensors monitor temperature, humidity, and foot traffic, providing data for building management systems (e.g., energy efficiency adjustments).
– Quality Impact: Adds functionality beyond aesthetics.
– LED-Integrated Tiles:
Tiles with built-in LED strips or backlit panels create dynamic lighting effects for commercial spaces.
– Quality Impact: Enhances adaptability for interior design.
Quality Improvements Through Technology
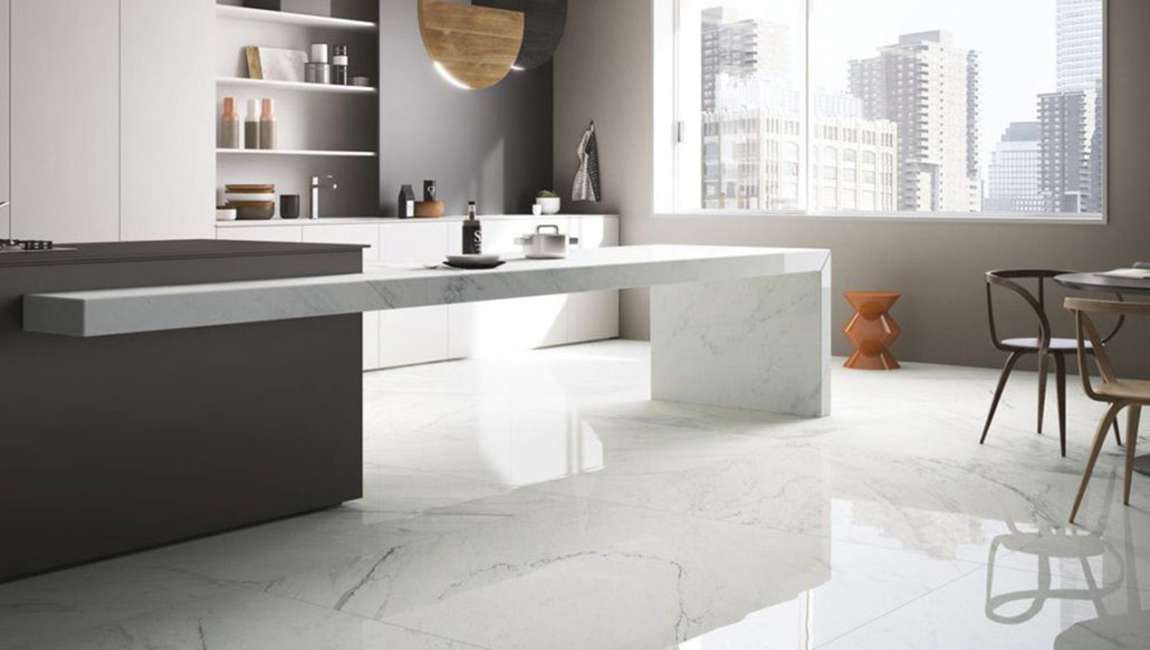

- Enhanced Durability
– Increased Resistance:
Advanced materials and coatings improve resistance to scratches, chemical stains, and thermal expansion. For example, porcelain tiles with a water absorption rate of <0.5% are ideal for outdoor use.
– Structural Integrity:
Precision-cut edges and robotic polishing ensure tiles withstand heavy loads and frequent use.
- Aesthetic Precision
– Customization:
Digital printing allows for bespoke designs, from subtle gradients to bold geometric patterns, tailored to client specifications.
– Color Consistency:
Automated color-matching systems ensure uniformity across large batches, eliminating batch-to-batch variations.
- Sustainability
– Recycled Materials:
Tiles made from recycled glass, porcelain waste, or industrial byproducts reduce environmental impact.
– Low VOC Emissions:
Eco-friendly glazes and adhesives comply with global sustainability standards (e.g., LEED certification).
- Reduced Waste
– Optimized Production:
AI-driven design software calculates tile layouts to minimize offcuts, lowering material waste.
– Circular Economy Models:
Manufacturers are exploring tile recycling programs to repurpose old tiles into new products.
Case Studies: Innovations in Action
Case Study 1: Self-Cleaning Tiles
– Company: Ceramica Flaminia (Italy)
– Technology: Hydrophobic nano-coating
– Outcome: Tiles repel water and dirt, reducing cleaning needs in hospitals and offices.
Case Study 2: 3D-Printed Textured Tiles
– Company: Crossville (USA)
– Technology: 3D printing for stone-like textures
– Outcome: Tiles mimic natural stone without environmental harm, used in luxury hotels.
Case Study 3: Energy-Efficient Production
– Company: Portinov (Spain)
– Technology: Solar-powered kilns
– Outcome: Reduced energy costs by 25% while maintaining tile quality.
Challenges and Considerations
- High Initial Costs:
Advanced technologies (e.g., 3D printing, AI systems) require significant upfront investment.
- Skill Gaps:
Manufacturers must train staff in operating and maintaining new equipment.
- Market Adoption:
Some clients may resist new technologies due to unfamiliarity or preference for traditional methods.
Future Trends in Slab Tile Technology
- Biodegradable Materials:
Research into compostable tiles for temporary structures or eco-friendly installations.
- AI-Generated Designs:
Machine learning algorithms will create unique, on-demand patterns for personalized tiles.
- Thermal Management:
Tiles with phase-change materials (PCMs) to regulate indoor temperatures, enhancing energy efficiency.
Conclusion
Advanced technologies are revolutionizing slab tile production, driving improvements in durability, aesthetics, and sustainability. From digital printing to smart IoT integration, these innovations address both functional and environmental challenges while meeting the evolving demands of commercial and residential design. As manufacturers continue to prioritize automation, eco-friendly practices, and cutting-edge materials, slab tiles will remain at the forefront of architectural innovation, blending form, function, and quality.
This article underscores how technological advancements are reshaping the ceramics industry, ensuring slab tiles remain a cornerstone of modern design for years to come.















نظرات ۰