Sustainable architecture has become a critical focus in the construction and design industries as the world grapples with the challenges of climate change, resource depletion, and environmental degradation. The goal of sustainable architecture is to minimize the environmental impact of buildings by using energy-efficient materials, reducing waste, and promoting eco-friendly practices. Among the materials that have gained prominence in sustainable architecture are slab tiles. These large-format tiles, known for their durability, versatility, and aesthetic appeal, play a significant role in reducing energy consumption and promoting sustainability. This article explores the role of slab tiles in sustainable architecture, focusing on their contribution to energy efficiency, resource conservation, and environmental responsibility.
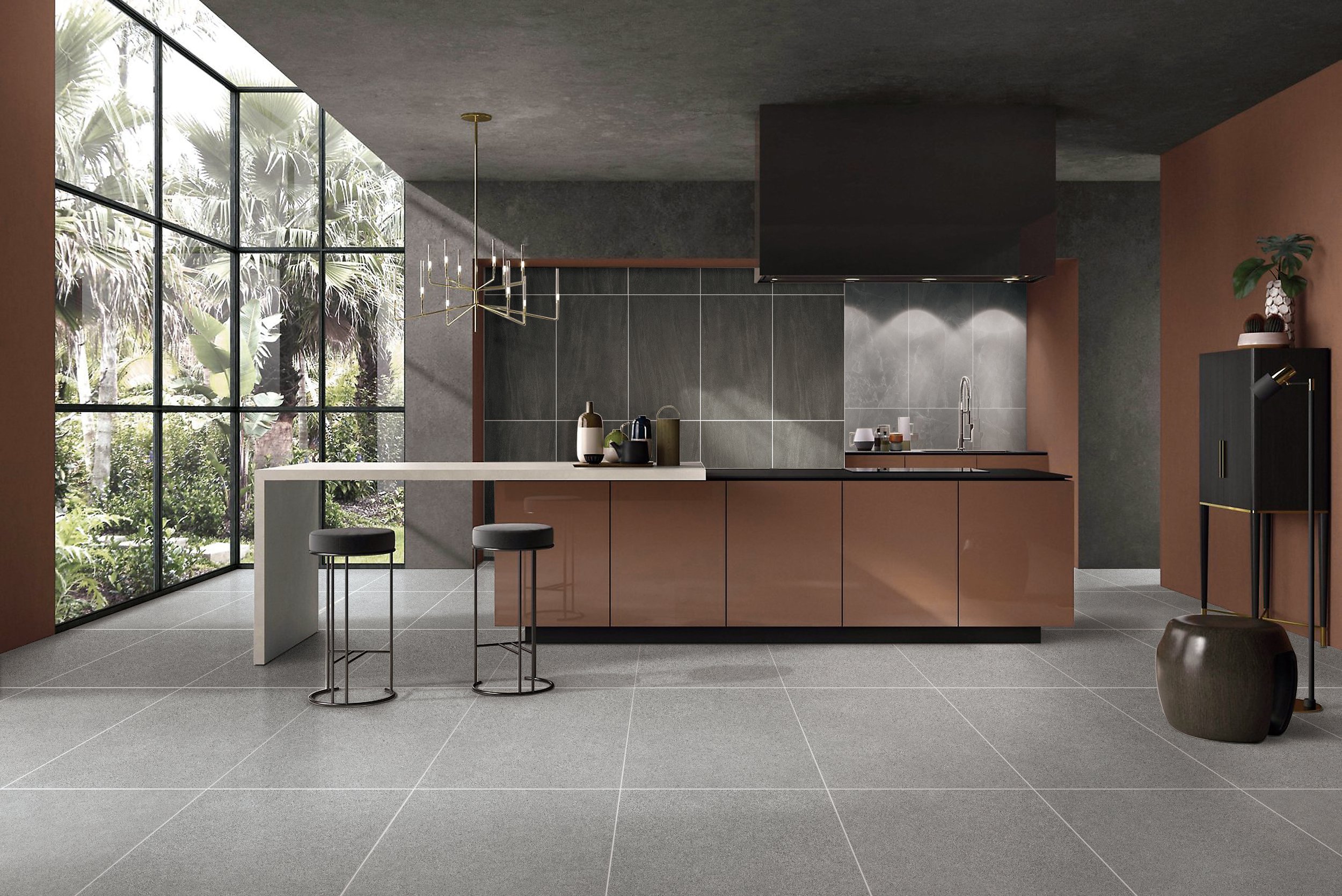

Understanding Sustainable Architecture
Sustainable architecture, also known as green architecture, is an approach to building design that seeks to minimize the negative environmental impact of buildings. This is achieved through the efficient use of materials, energy, and space, as well as the integration of renewable energy sources and eco-friendly technologies. The key principles of sustainable architecture include:
- Energy Efficiency: Reducing energy consumption through the use of energy-efficient materials, insulation, and renewable energy sources.
- Resource Conservation: Using materials that are sustainable, recyclable, and have a low environmental impact.
- Environmental Responsibility: Minimizing waste, reducing carbon emissions, and promoting biodiversity.
- Durability and Longevity: Designing buildings and using materials that are durable and require minimal maintenance over time.
- Indoor Environmental Quality: Ensuring that buildings provide healthy and comfortable living environments for occupants.
Slab Tiles: An Overview
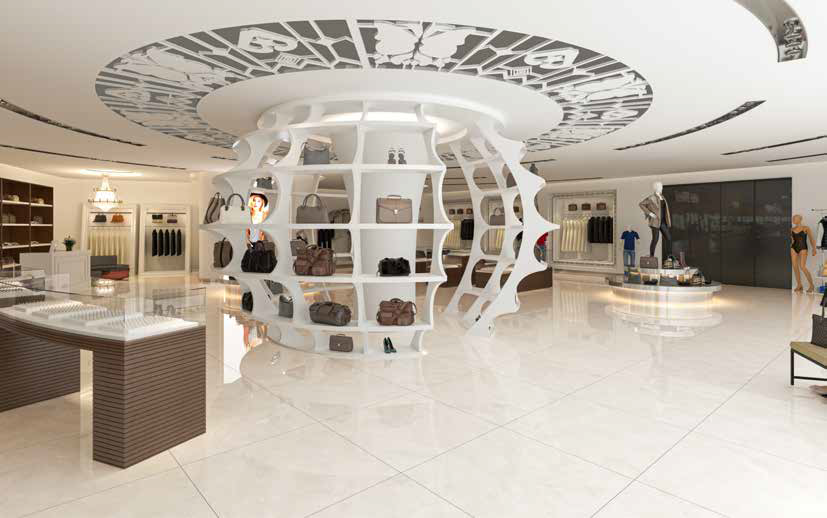
Slab tiles are large-format tiles, typically measuring 120×120 cm or larger, that are thinner and lighter than traditional tiles. They are made from materials such as ceramic, porcelain, or natural stone and are known for their seamless appearance, durability, and versatility. Slab tiles are widely used in both interior and exterior applications, including walls, floors, countertops, and facades.
Key characteristics of slab tiles include:
- Large Format: The large size of slab tiles reduces the number of grout lines, creating a smooth and continuous surface.
- Durability: Slab tiles are highly resistant to scratches, stains, and moisture, making them ideal for high-traffic areas.
- Versatility: They are available in a wide range of colors, textures, and finishes, allowing for diverse design possibilities.
- Low Maintenance: Slab tiles are easy to clean and maintain, requiring only regular wiping to keep them looking pristine.
- Eco-Friendly Production: Many slab tiles are manufactured using sustainable practices, such as recycling materials and reducing water and energy consumption during production.
The Role of Slab Tiles in Sustainable Architecture
Slab tiles contribute to sustainable architecture in several ways, from reducing energy consumption to promoting resource conservation. Below, we explore the key roles of slab tiles in sustainable design:
- Energy Efficiency
One of the most significant contributions of slab tiles to sustainable architecture is their ability to enhance energy efficiency. Slab tiles can be used in conjunction with energy-efficient building systems to reduce heating and cooling costs.
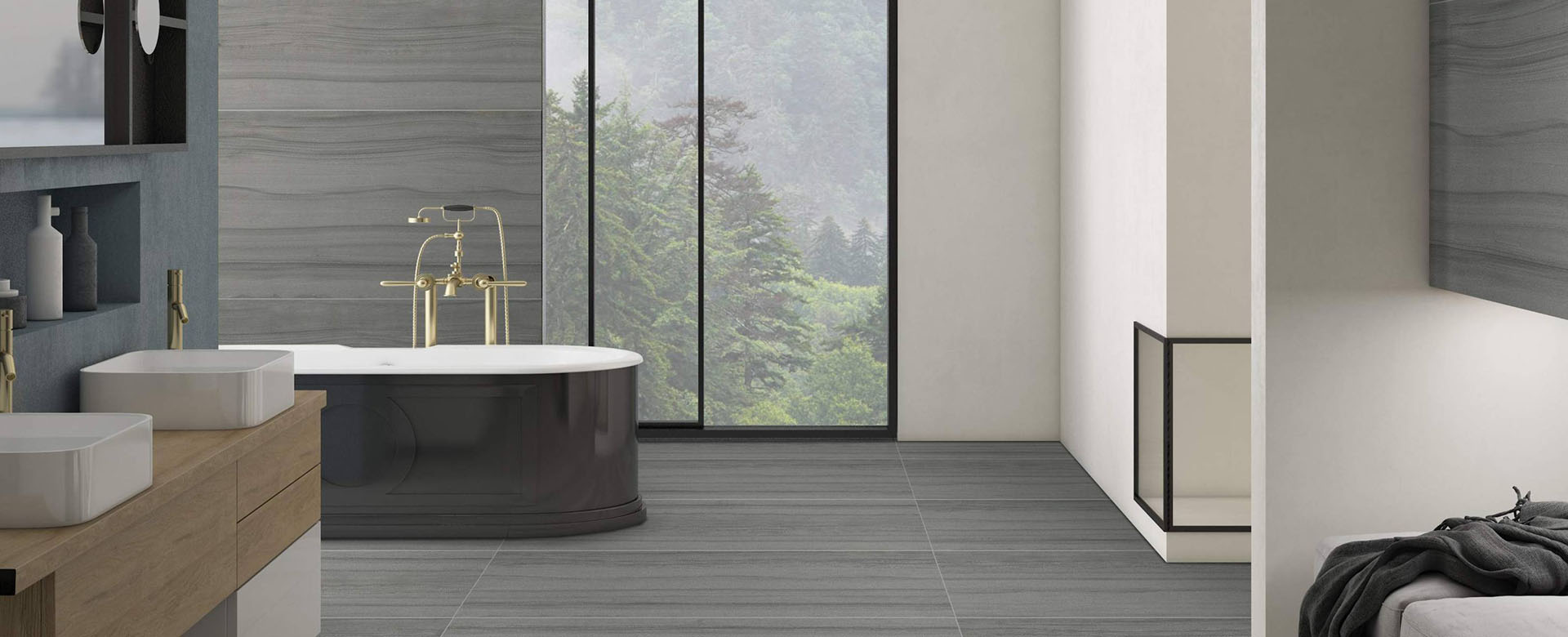
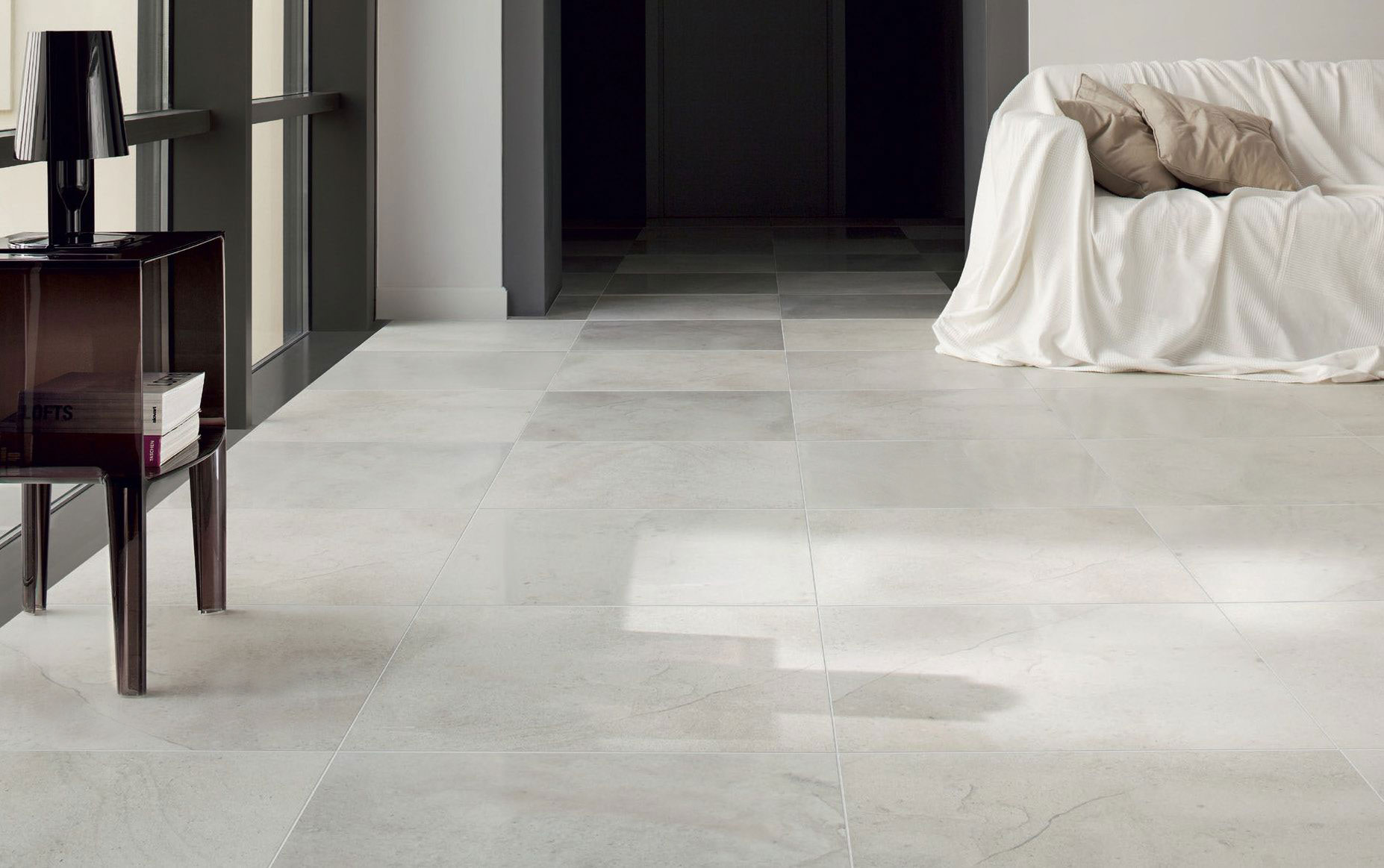
– Thermal Insulation: Slab tiles have excellent thermal properties, helping to regulate indoor temperatures. When used on floors and walls, they can absorb heat during the day and release it slowly at night, reducing the need for artificial heating and cooling.
– Reflective Surfaces: Light-colored slab tiles can reflect sunlight, reducing heat absorption and keeping indoor spaces cooler. This is particularly beneficial in hot climates, where it can significantly reduce the need for air conditioning.
– Integration with Underfloor Heating: Slab tiles are highly compatible with underfloor heating systems, which are more energy-efficient than traditional heating methods. The tiles’ thermal conductivity ensures even heat distribution, enhancing comfort while reducing energy consumption.
- Resource Conservation
Slab tiles contribute to resource conservation by using sustainable materials and manufacturing processes. Many manufacturers are adopting eco-friendly practices, such as recycling waste materials and reducing water and energy consumption during production.
– Recycled Materials: Some slab tiles are made from recycled materials, such as glass, ceramics, and industrial waste. This reduces the demand for virgin materials and minimizes waste.
– Longevity and Durability: Slab tiles are highly durable and can last for decades with minimal maintenance. This reduces the need for frequent replacements, conserving resources and reducing waste.
– Low Water Consumption: The production of slab tiles typically requires less water compared to other building materials, such as concrete or natural stone. This makes them a more sustainable choice, particularly in regions facing water scarcity.
- Environmental Responsibility
Slab tiles promote environmental responsibility by reducing carbon emissions and minimizing waste. Their production and use align with the principles of sustainable architecture, making them an eco-friendly choice for builders and designers.
– Low Carbon Footprint: The production of slab tiles generates fewer carbon emissions compared to traditional building materials, such as cement or steel. Additionally, their lightweight nature reduces transportation costs and emissions.
– Waste Reduction: The large format of slab tiles reduces the amount of waste generated during installation. Fewer tiles are needed to cover a given area, and the precision cutting of tiles minimizes offcuts.
– Non-Toxic Materials: Slab tiles are made from natural materials and do not emit harmful chemicals or volatile organic compounds (VOCs), ensuring a healthy indoor environment.
- Contribution to Green Building Certifications
The use of slab tiles can contribute to achieving green building certifications, such as LEED (Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design) or BREEAM (Building Research Establishment Environmental Assessment Method). These certifications recognize buildings that meet high standards of sustainability and energy efficiency.
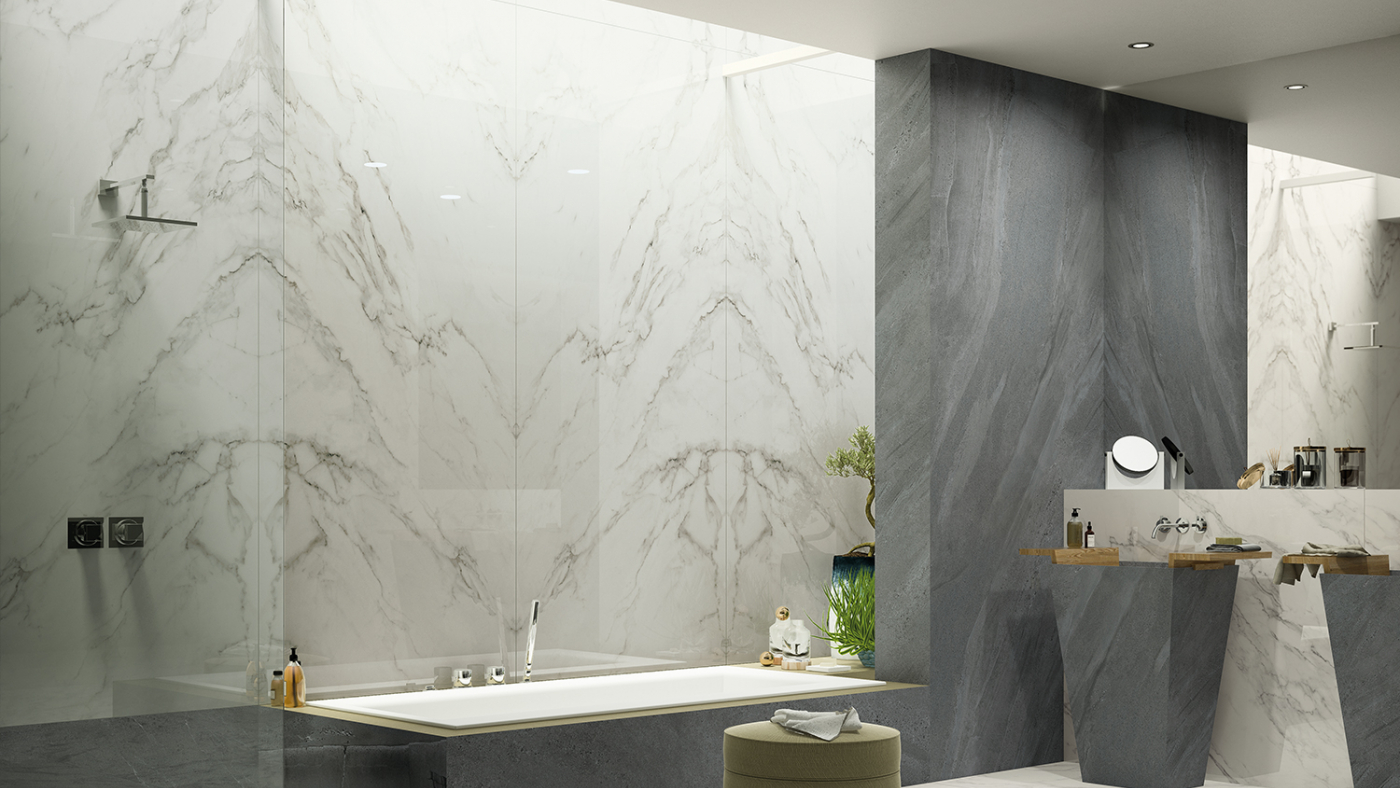

– Energy Performance: The thermal properties of slab tiles can improve a building’s energy performance, contributing to points in the energy efficiency category of green building certifications.
– Material Selection: The use of eco-friendly slab tiles made from recycled or sustainable materials can earn points in the materials and resources category.
– Indoor Environmental Quality: The non-toxic nature of slab tiles and their contribution to thermal comfort can enhance indoor environmental quality, another key category in green building certifications.
Case Studies: Slab Tiles in Sustainable Architecture
To illustrate the role of slab tiles in sustainable architecture, let’s explore a few case studies:
- Energy-Efficient Residential Building
In a residential building designed for energy efficiency, slab tiles were used for flooring and walls throughout the home. The light-colored tiles reflected sunlight, reducing heat absorption and keeping the interior cool during the summer. The tiles’ thermal mass helped regulate indoor temperatures, reducing the need for artificial heating and cooling. The building achieved LEED Gold certification, thanks in part to the energy-efficient properties of the slab tiles.
- Eco-Friendly Office Complex
An office complex designed with sustainability in mind used slab tiles for its exterior facade and interior spaces. The tiles were made from recycled materials, reducing the project’s environmental impact. The reflective surface of the tiles minimized heat gain, lowering the building’s cooling costs. The project earned BREEAM certification, with the slab tiles contributing to points in the materials and energy efficiency categories.
- Sustainable Public Library
A public library designed as a model of sustainable architecture incorporated slab tiles in its flooring and countertops. The tiles’ durability ensured that they could withstand heavy foot traffic, reducing the need for frequent replacements. The library’s energy-efficient design, which included underfloor heating integrated with slab tiles, significantly reduced energy consumption. The project received recognition for its innovative use of sustainable materials and energy-efficient systems.

Conclusion
Slab tiles play a vital role in sustainable architecture, offering a combination of energy efficiency, resource conservation, and environmental responsibility. Their thermal properties, durability, and eco-friendly production processes make them an ideal choice for builders and designers seeking to create sustainable and energy-efficient buildings.
As the demand for sustainable architecture continues to grow, slab tiles will remain a key material in the construction industry. Their ability to reduce energy consumption, conserve resources, and promote environmental responsibility aligns perfectly with the principles of sustainable design. By incorporating slab tiles into their projects, architects and designers can contribute to a more sustainable and energy-efficient future.













نظرات ۰